Home > News
Health info.
The Health Protective Benefits of Massage:
For the skin :
Among the many tissues of the human body, the skin includes sebum glands, sweat glands, blood vessels, and nerve endings. With these and other components, the skin has temperature regulatory, excretory, and respiratory functions, and, of course, it is our outermost layer, allowing us to sense and offering protection. Medically, appropriate stimulation of the skin (massage) can enlarge the pores, aid the secretion of sebum, the fat in our skin that makes us look youthful, and at the same time benefits respiration and excretion through sweating, two very important functions. Massage can also improve circulation, keeping the skin ruddy, elastic and smooth.
For the circulatory system :
One cycle of the "circulatory system" involves the following three steps: 1) The blood from the various body tissues drains to the vena cava, whence the heart pumps it into lungs to exchange its carbon dioxide content for oxygen, 2) the carbon dioxide rich air in the lungs is exhaled, 3) the oxygen rich blood from the lungs is then pumped by the heart through the aorta to the various tissues of the body. Simply stated, the circulatory system undertakes one of the body's most important transport functions. Not only does it remove the carbon dioxide from the blood and carry oxygen to the body tissues, it also takes other products of metabolism to the kidneys and liver, which excrete them from the body. Medically speaking, massage can help enlarge blood vessels, quickening the flow of blood, relieving the burden on the heart and generally allowing the circulatory system to run more smoothly.
For the muscles:
When the muscles suffer exhaustion or undue strain, local muscle stiffness is a common result, which make turn into muscle pain, soreness, and other symptoms. In the long term, excessive muscle strain may lead to pathological changes in the internal organs. From a medical perspective, massage can loosen up stiff muscles, and can increase the flow of circulation, restoring muscle elasticity and strength and also aiding exercise.
For the nervous system :
In its entirety, the human nervous system includes the brain (the cerebrum, the cerebellum, and the skull), the spinal cord, and the nerves: in total three parts. In a regular person, there are twelve pairs of nerves that connect to the eyes, ears, tongue, nose and facial muscles, shoulder muscles and internal organs, etc.; from the spinal cord issue thirty one pairs of spinal nerves, which are distributed to the trunk, the limbs, and the internal organs. The nerves transmit sensory information gathered from outside stimulation and transmit it to the spinal cord or the brain; they can also issue orders from the brain or spinal cord to parts of the body that will perform as actions the decisions of the brain. In medical terms, massaging the skin stimulates nerve endings, and for this reason appropriate massage, whether it causes sensations of relaxation, comfort, or soreness, will cause the transmission of a mass of sensory information along the spinal cord to the brain, a very healthy stimulation that helps to adjust body functioning, allows the restoration of a proper state of balance and maintains the stability of the nervous system.
For the Meridians
Concentrating on Chinese medicine, the meridians are the lifelines along which the vital energy of the body is transported. An appropriate intensity of massage aids this system in the same way as the circulatory system by making it more free flowing. A more freely flowing meridian system will be directly reflected in the human body's vital essence "ching", vital energy "chi", and vital spirit "shen".
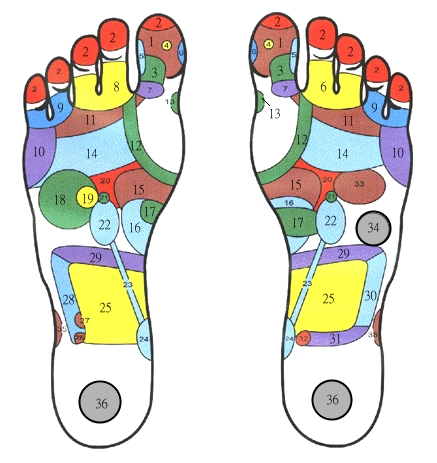 |
TRADITIONAL MEDICAL SYSTEM ANALYSIS
1.BRAIN-insomnia, headache, dizzy, high blood pressure.
2. FRONTAL SINUSES - headache, dizzy,eye nose
3.CEREBELLUM- prevent apoplexy, insomnia
4. PITUITARY GLAND –control endocrine gland
5. TEMPORAL AREA –migraine, paralysis, insomnia
6. NOSE – rhinitis, nasal congestion
7. NECK –stiff, sprain
8. EYE – myopia, cataract
9. EAR – hard of hearing, tinnitus
10. SHOULDER – shoulder, feel weak
11. TRAPEZIUS – shoulder arthritis, ache
12. THYROID GLANDS – arthritis, rheumatism, arrhythmia
13. PARATHYROID
14. LUNGS AND BRONCHI –asthma, cough, cold, pneumonia
15. STOMACH – gastralgia, gastric ulcer
16. DUODENUM – dyspepsia, duldenal ulcer
17. PANCREAS – control insulin, blood sugar, control diabetes
18. LIVER-cirrhosis, fatigue, insomnia, liver
19. GALL BLADDER
20. SOLAR PLEXUS-
21. ADRENAL GLANDS-
22. KIDNEYS - nephritis, rheumatism,arthritis, high blood pressure,
arteriosclerosis
23. URETERS
24. BLADDER –frequent micturition, dysuria, calculus, cystitis
25. SMALL INTESTINES – malnutrition, diarrhoea, fatigue
26. Appendix –appendicitis, abdominal distention
27. ILEOCECAL valve-
28. ASCENDING COLON- diarrhea, constipation
29. TRANSVERSAL COLON- colitis, diarrhea
30. DESCENDING COLON - colitis, diarrhea
31. RECTUM – constipation, hemorrhoids
32. ANUS - constipation, hemorrhoids
33. HEART –myocardial infarction, arrhythmia, arteriosclerosis
34. SPLEEN- poor appetite, poor resistance
35. KNEE -
36. GENITAL GLANDS –sexual dysfunction, sterility, menopausal syndrome